

Molecular Weight of polymers dispersed in solution: On a sample volume of 10-40 µL, the instrument can determine a range between 1kDa to 25 MDa. It can analyse a wide range of suspension concentrations (0.1 ppm to 40% v/v depending on the sample type). The light scattering: ccording to the semi-classical light scattering theory Berne and Pecora, 'Dynamic Light scattering' John Wiley, 1975, when light impinges on matter, the electric field of the light induces an oscillating polarization of electrons in the molecules. It claims an accuracy of 0.12 µm.cm/V.s and a sensitivity of 10 mg/mL (BSA). determination of the number-weighted mean radius and polydispersity from dynamic light-scattering data. Minimum sample volume required is 175 µL. Intensity of the scattered light fluctuates. Zeta Potential: It can measure wide range of zeta potentials for particles in the size range 1 nm – 100 µm, depending on the type of sample.
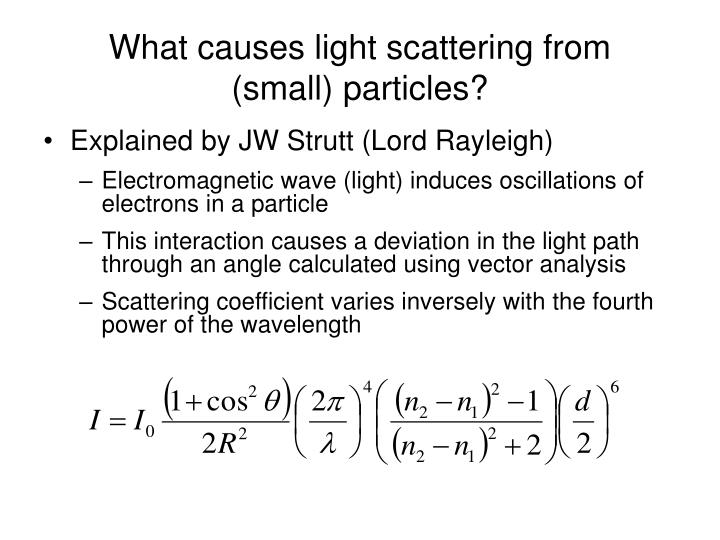
It claims an accuracy of ☒% with a precision of ☑%. Particle Size and Molecular Size: It can measure size between 0.3 nm to 6 µm with a minimum volume 10 µL of sample suspension. dynamic light scattering: applications of photon correlation spectroscopy Light Scattering Spectroscopy. nucleon-nucleon correlations in elastic electron scattering from light nuclei. Viral vectors employed in gene therapy applications require thorough analytical characterization in order to assure consistent safety, efficacy and. A 32-bit single CPU as well as the Light version is available to researchers. It can also be used to probe the behaviour of complex fluids such as concentrated polymer solutions. Light Scattering Theory - Book 5: p.40-81. ppt, on defects in crystals, annual, 3 / 69-2 / 70, 24 : 33577. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) principle can be used to determine the size distribution profile of small particles in suspension or polymers in solution. When the potential is low, attraction exceeds repulsion and the dispersion will break and flocculate. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), sometimes referred to as Photon Correlation Spectroscopy or Quasi-Elastic Light Scattering, is a technique classically used for measuring the size of particles typically in the sub-micron region, dispersed in a liquid. For molecules and particles that are small enough, a high zeta potential will confer stability, i.e., the solution or dispersion will resist aggregation. The zeta potential indicates the degree of repulsion between adjacent, similarly charged particles (e.g., the vitamins) in a dispersion. The significance of zeta potential is that its value can be related to the stability of colloidal dispersions (e.g., a multivitamin syrup). It can determine particle size distribution, particle zeta potential (related to the magnitude of the electrical charge at the particle surface) and molecular weight of large polymeric substances dispersed in water. The DLS Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analyzer is a user-friendly system for colloidal, nanoparticulate and macromoleculer characterization.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
